Types of IoT Sensors : A Complete Guide to 16 Essential Sensors
Discover the top types of IoT sensors in 2024, including temperature, pressure, proximity, and more. Learn how these 20 essential sensors are transforming industries with innovative applications and benefits
Prevalence and Importance of IoT Sensors
Sensors in IoT have become a common tool in various applications. Smartphones have significantly reduced the cost of the sensors used in electronics products and the industrial sectors. As IoT technology becomes more integrated into people’s daily lives, sensors are more visible than ever. The IoT environment is changing significantly, and the IoT-connected devices are predicted to be 29.42 billion in 2030. This expansion is driving the IoT sensor market, which is expected to hit a mind-boggling increase of $113.01 billion by 2032.
What Are IoT Sensors?
Sensors in IoT are tangible objects that are employed to collect information from their environment and pass it on to other connected systems or devices through the Internet. These sensors are critical in the process of making the physical world more digital or connected and are part of the larger IoT system. One type of sensor is designed for the collection of certain kinds of information, and all of them are used in the creation of smart systems.
Main Characteristics of IoT Sensors
- Data Collection: IoT sensors record a vast number of real-world phenomena, including temperature, humidity, and air quality, as well as movement, light, sound, and pressure.
- Connectivity: These sensors can be wired or wireless and are expected to interface with the Internet or other devices. It also helps in the transfer of collected data to other central processing units or other devices for analysis and decision-making.
- Embedded Technologies: Some IoT sensors are coupled with other technologies such as RFID, GPS, accelerometers or gyroscopes to offer more value to the data collected.
- Applications: IoT sensors are used in different sectors including agriculture, health, manufacturing, transport, and smart homes. These sensors make possible more effective, automatic and smart systems by providing valuable information about the real environment.
- Interconnected Systems: Sensors when used in conjunction with other IOT devices play a role in the creation of networks of systems where data is exchanged for decision-making. For instance, in smart cities, some devices help to track traffic, weather conditions, and energy consumption to improve services.
Classification of Sensors
Passive and Active Sensors
- Passive Sensors: These sensors cannot function on their own to sense input. Some examples include accelerometers, soil moisture sensors, “water level” sensors and “temperature sensors”.
- Active Sensors: These sensors can sense input on their own. They include radar, sounder, and laser altimeter sensors.
Analog and Digital Sensors
- Analog Sensors: The output of these sensors is a continuous function of the input parameter. Some of them include temperature sensors, light-dependent resistors, analog pressure sensors and analog hall effect sensors.
- Digital Sensors: These sensors respond in a simple yes or no fashion and are intended to eliminate the problems associated with analog sensors. They also include extra electronics for signal conversion from analog to digital bits. Some of them are Passive Infrared (PIR) sensors and digital temperature sensors such as the DS1620.
Scalar & Vector Sensors
- Scalar Sensors: These sensors are capable of sensing input quantity without direction or orientation of input. The quantity produced by them depends on the size of the input parameter. They include temperature, gas, strain, color, and smoke sensors.
- Vector Sensors: the output of vector sensors depends on the value of the input parameter as well as the direction of this value. These include accelerometer, gyroscopes, magnetic field sensors and motion detectors.
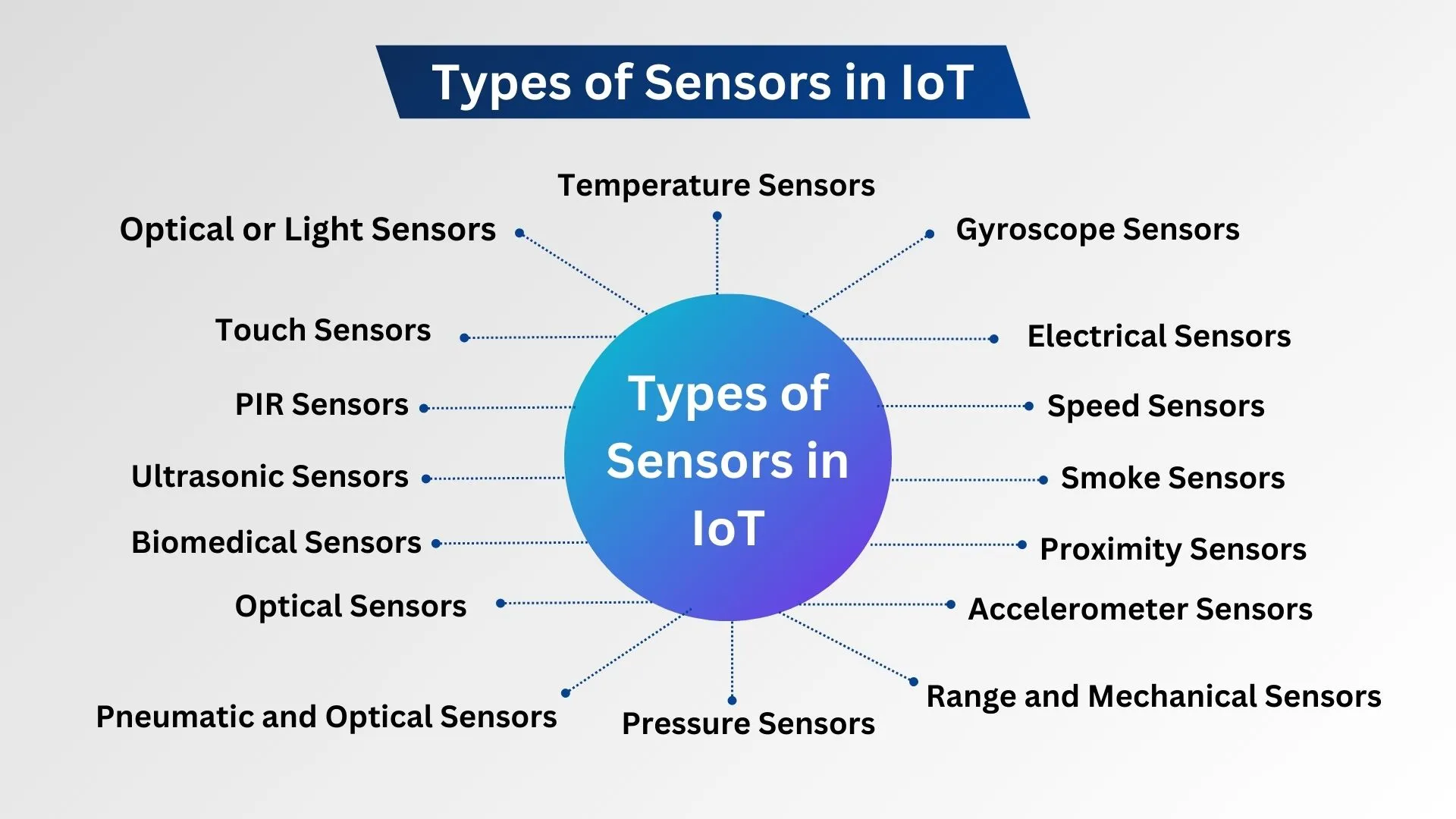
Types of IoT Sensors
Optical or Light Sensors
They are also known as photo or photon sensors because they are used to measure changes in light intensity. The most popular light sensor is the Light Dependent Resistor (LDR), where the resistance of the sensor decreases with the increase of the intensity of the ambient light and vice versa. Optical sensors work through a process of converting light into electricity and can be used in many industries. In the automotive industry, optical sensors are used to identify road signs, objects, and other features that help drivers during parking and driving. These sensors are especially important for the development of self-driving automobiles. In smartphones, optical sensors like the ambient light sensors adjust the brightness of the screen to save battery power. Further, in the biomedical sectors, optical sensors are applied in breath tests and pulse oximetry, which is also helpful in the development of healthcare technology.
Temperature Sensors
Temperature sensors are used to measure the heat in the environment and it changes the temperature into an electrical signal normally in the form of voltage. These sensors are applied in air conditioning systems, refrigeration systems, smart thermostats, and in agricultural and food industries.
Use Cases of Temperature Sensors:
These sensors are used in various industries to improve accuracy in data acquisition and decision-making for automatic control systems.
- Air Conditioning and Refrigeration: Thermostats control the heating and cooling in air conditioning systems and refrigerators for the right temperature values.
- Smart Buildings: These sensors help in monitoring the temperature of air and water within smart homes as well as smart buildings for better regulation of the environment or climate.
- Food Industry: Thermometers assist in checking the right temperature for food products to help them be within the right temperature when in transit.
- Agriculture: In farming, temperature sensors are used to measure the conditions of the soil and air, especially in controlled environment farming systems and give farmers an alert when the temperatures change in ways that may harm the crops.
Top 5 optical or light sensors
- Photodiodes
- Photoresistors (LDR)
- Phototransistors
- Charge-Coupled Devices (CCD)
- Infrared Sensors (IR Sensors
Pressure Sensors
The pressure (IoT) sensors measure the variation of pressure with a reference pressure, convert it into an electrical form, and send it to the control system. These sensors are applicable in different industries.
Use Cases of Pressure Sensors:
- Leak Detection in Plumbing Systems: Detects leaks by calculating pressure changes in water lines and determines which lines have leaked.
- Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems Monitoring: Checks that the pressure of machines is within the required pressure level to support safety and productivity.
- Aviation: Measures altitude and airspeed in aircraft for ease in maneuvering as well as safety during flying.
- Oil and Gas Industry: Measures pressure of well and borehole in oil wells, which is used to control the drilling and extraction of the well.
Touch Sensors
In touch sensors, there are ways to identify whether there is a finger or a stylus on the surface of a material. They are generally classified into two types: resistive and capacitive. Most of the touch sensors of today are capacitive because of their higher precision and better signal-to-noise ratios.
Gyroscope Sensors
Gyros are used in conjunction with accelerometers to measure specific angular rotational velocity (speed in a direction). While accelerometers measure linear acceleration, gyroscopes measure the rotation giving more information about the motion. Gyroscopes are available in various forms and characteristics such as size, performance, and working conditions.
Use Cases of Gyroscope Sensors:
- Space Shuttles: High-accuracy ring laser gyroscopes are used for navigation.
- Aircraft and Race Cars: AGM fibre optic gyroscopes are used to measure high-accuracy angular motion for stability and control.
- Consumer Electronics: Vibration gyroscopes are used in car navigation systems, digital cameras, and game controllers.
- Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS): Measures “yaw rate” (Yaw rate could refer to the rate at which a rigid body’s heading angle changes, indicating its angular velocity as it rotates about its vertical axis. This measurement is typically expressed in radians or degrees per second.), and rollover for the safety of the vehicle.
- Virtual Reality (VR): Improves the interaction experience by following the head motions in the gaming controllers and the virtual reality helmets.
Range and Mechanical Sensors
Short-range sensors employ electrical capacitance, inductance and magnetic methods while long-range sensors use energy waves including radio waves, sound waves, and lasers.
Some mechanical sensors include micro-switches that need a force to act on them to work. These switches transform mechanical force into an electrical signal and are therefore ideal for use in mechanical actuation applications.
Electrical Sensors
Proximity sensors can be of contact or non-contact types but are mostly used electrically. Contact sensors work by closing a circuit between the “sensor” and “component”. Non-contact electrical proximity sensors employ the principles of induction for sensing metals and capacitance for sensing non-metals.
Pneumatic and Optical Sensors
There are pneumatic proximity sensors that work by sensing the interruption of a flow of air. These are contact types of sensors and are widely used where the application involves contact and light or other factors are not allowed.
Optical proximity sensors operate by breaking an infrared beam that falls on a light-sensitive element like the photocell. These non-contact sensors have to be controlled for environmental variables, for instance, light or dust in the air which may affect the sensors.
Speed Sensors
Velocity sensors detect the velocity of moving bodies or vehicles. Some of them are wind speed sensors, speedometers, and ground speed radar. They are very essential in use in areas that need the tracking of velocity in real-time.
PIR Sensors
Passive Infrared (PIR) sensors are devices that measure the radiation emitted by objects within their field of view. They are mostly employed in security systems, lighting control, and any other area that needs to monitor the movement of people.
Ultrasonic Sensors
Ultrasonic sensors are similar to SONAR or RADAR systems and operate by emitting high-frequency sound waves to identify objects and their distance. These sensors are normally applied in detecting obstacles and measuring distances in robotics and automotive contexts.
Accelerometer Sensors
Accelerometers became popular when Apple started using them in iPhones for orientation and motion sensing. These sensors determine the variation in velocity concerning the Earth’s surface. The various types of accelerometers include; Capacitive, Piezoelectric, and MEMS (Micro Electro Mechanical System).
Use Cases of Accelerometer Sensors:
- Inertial Navigation Systems: Applied in the missiles and aircraft for accurate directions.
- Drones: They may be used to support flight simulation by detecting tilting and orientation changes.
- Anti-Theft Protection: Used to detect the movement of static objects to activate alarms.
- Vibration Monitoring: Senses motion in rotating equipment like smartphones and tablets.
- Wearables: Supervises physical motions in fitness gadgets and health care equipment.
Biomedical Sensors
Biomedical IoT sensors are intended for the detection of various physical and biological variables in the living organism. These sensors find application in healthcare for diagnostic, monitoring, and therapeutic purposes by giving real-time information about body temperature, blood glucose level, CO2 and many more.
Use Cases of Biomedical Sensors:
- Sports Medicine and Physical Therapy: Assists in Studying the body motions and distribution of forces to avoid problems with the musculoskeletal system.
- Diagnostics: Diagnoses physiological or biochemical indicators such as proteins, enzymes or other molecules in body fluids for evaluation of health status.
- Body Temperature Monitoring: Uses in fever and other clinical assessment by measuring body temperature.
- Remote Patient Monitoring: Allows patients to deal with chronic diseases or post-surgery treatment, being in touch with doctors from far away and remote locations.
Motion Detection Sensors
PIR IoT sensors are intended for the detection of physical movement in a particular zone and its transformation into a signal for the control systems.
Common in security systems these are devices that use infrared rays, ultrasonic waves, and microwaves to detect motion and classify the movements.
Use Cases of Motion Sensors:
- Home Security: Alerts and alarms or notifications when there is an intruder within the vicinity.
- Energy Efficiency: Switches on lights when there is movement in the area and switches it off when there is no movement in the area.
- Automatic Doors: Recognizes people on the sidewalks, in shops, and in airports, which causes doors to open.
- Video Surveillance: Switches cameras on when motion is sensed, minimizes storage and review of video footage.
- Fitness Trackers: Records user interaction, measures steps taken, records sleep, and records physical activity.
Smoke Sensors
These IoT-based sensors are crucial in safety solutions in different places, including business entities, homes, and factories. These sensors detect smoke, flames, or dangerous gases and sound a bell to notify the people inside the building. When smoke sensors are connected to the IoT systems, they are capable of performing actions like opening the dump fans, unlocking the evacuation doors, and triggering the alarms to alert the people; this also helps in controlling fire.
Use Cases of Smoke Sensors:
- Protect plants, fruits, vegetables and other structures in greenhouses and other farming structures.
- Identify smoke in public transport vehicles to avoid fire outbreaks in the cabins that convey passengers.
- Recognize wildfires and initiate early actions to control fire outbreaks.
- Avoid fire losses and disruptions of telecom services in facilities and cell towers.
- Supervise commercial kitchens to reduce fire dangers from cooking appliances.
Proximity Sensors
These sensors employ GPS and other techniques to “capture” an object and cause something to happen such as sending signals to activate a process or alarm. These sensors measure the distance between the object and the sensor and whether there is an object within a specific distance. Automotive, retail and industrial industries are the most common areas where proximity sensors are used.
Use Cases of Proximity Sensors:
- Give feedback with a beep when a vehicle or car is reversing and is close to an object.
- Use mobile marketing to target customers with marketing promotions in the vicinity of a retail store.
- Facilitate the identification of available parking spaces in airports and shopping mall.
- Control the amount of liquid flow and storage.
- This should be done when approached to enhance waste disposal in trash bins and compactors.
- Switch on ATMs during the approach by a user for transactions.
Optical Sensors
Optical sensors detect the intensity of light and the various kinds of electromagnetic energy in the environment and provide this as a format of signals. These sensors are used where there is a need to have immunity to electrical interference such as in transport, oil and gas, medical imaging, and manufacturing industries.
Use Cases of Optical Sensors:
- Measuring the ambient light to control the brightness in displays and smartphones.
- Also applied in color sorting machines.
- Scan and interpret barcodes for checkout and stock tracking in stores.
- Endoscopes and Ophthalmic instruments are used in the treatment of diseases.
Flow Sensors
Flow sensors are used to determine the speed of a liquid or a gaseous substance through a given system. They are used in diverse industries like manufacturing, energy, and environmental research to monitor and control fluid flow. Turbine, vortex and electromagnetic flow sensors are used for different fluids and applications.
Use Cases of Flow Sensors:
- Use in controlling and managing fluid within industrial automation and chemical processing industries.
- Monitor water flow in treatment plants and air quality in environmental check-ups.
- Control the rate of natural gas and oil in energy generation and distribution.
- Maintain the correct flow measurement of fuel and hydraulic fluid in the aircraft.
Humidity Sensors
Humidity sensors are used to calculate humidity. These sensors are used in conjunction with temperature sensors in environments where accurate measurements of environmental conditions are needed such as heating, ventilating and air conditioning systems, and in meteorological sciences.
Use Cases of Humidity Sensors:
- HVAC systems of homes as well as commercial buildings should be regulated in terms of humidity.
- Employed in weather stations to indicate and forecast climate circumstances.
- Maintain proper humidity in the processes of manufacturing where the working conditions are critical (like in metal molting industries).
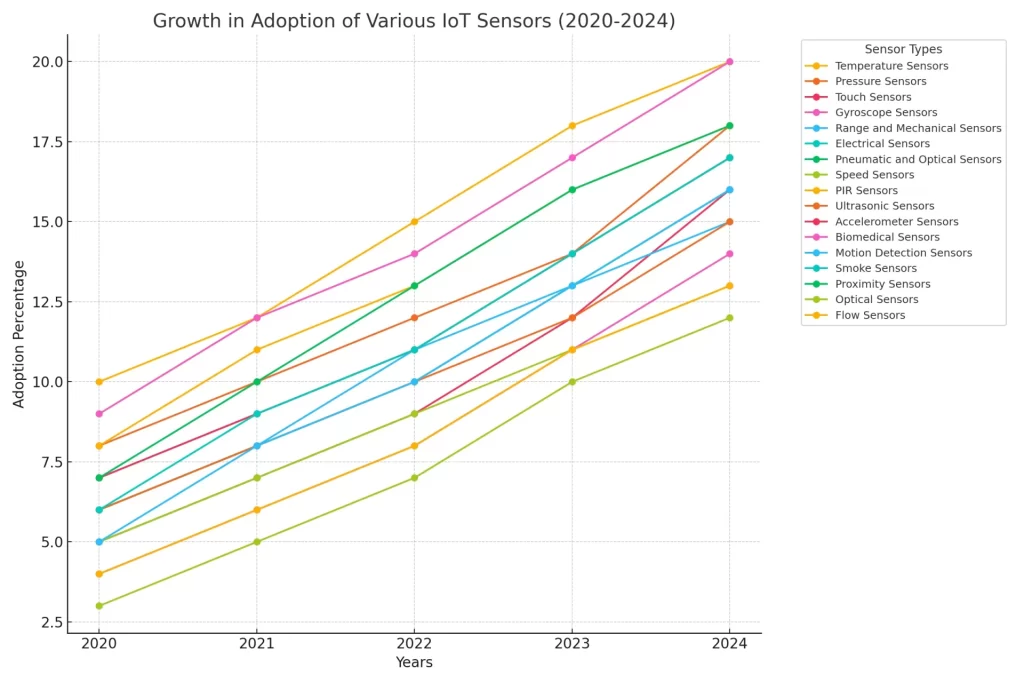
Growth In Adoption Of Various IoT Sensors (2020-2024)
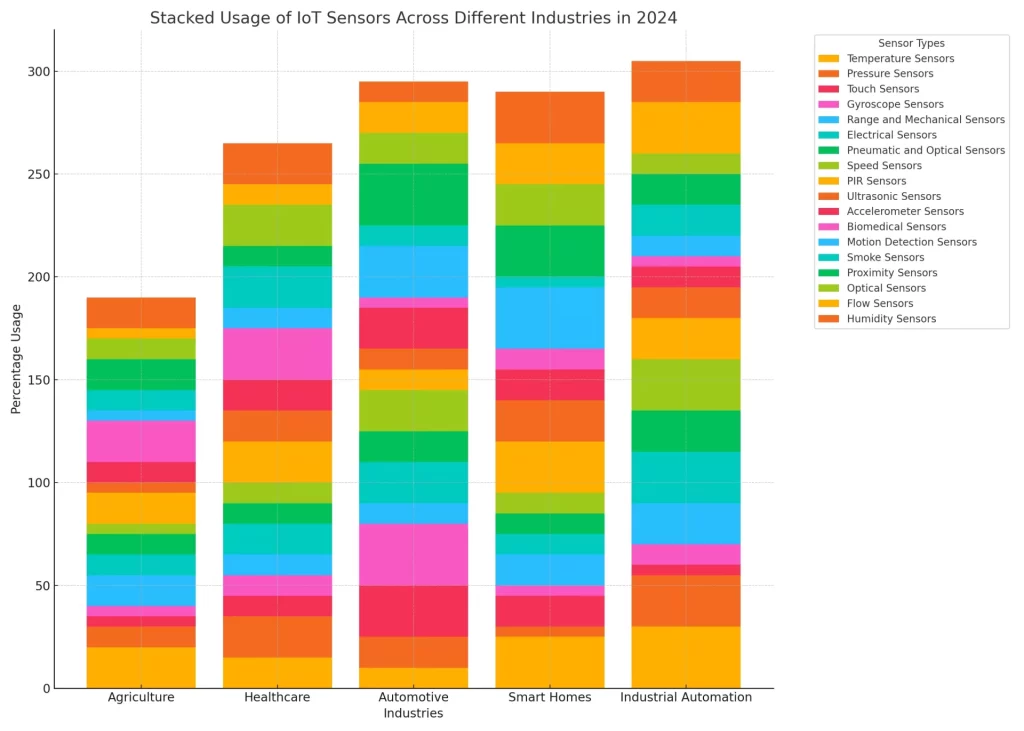
Stacked Usage Of IoT Sensors Across Different Industries in 2024
This graph shows Stacked Usage Of IoT Sensors Across Different Industries in 2024
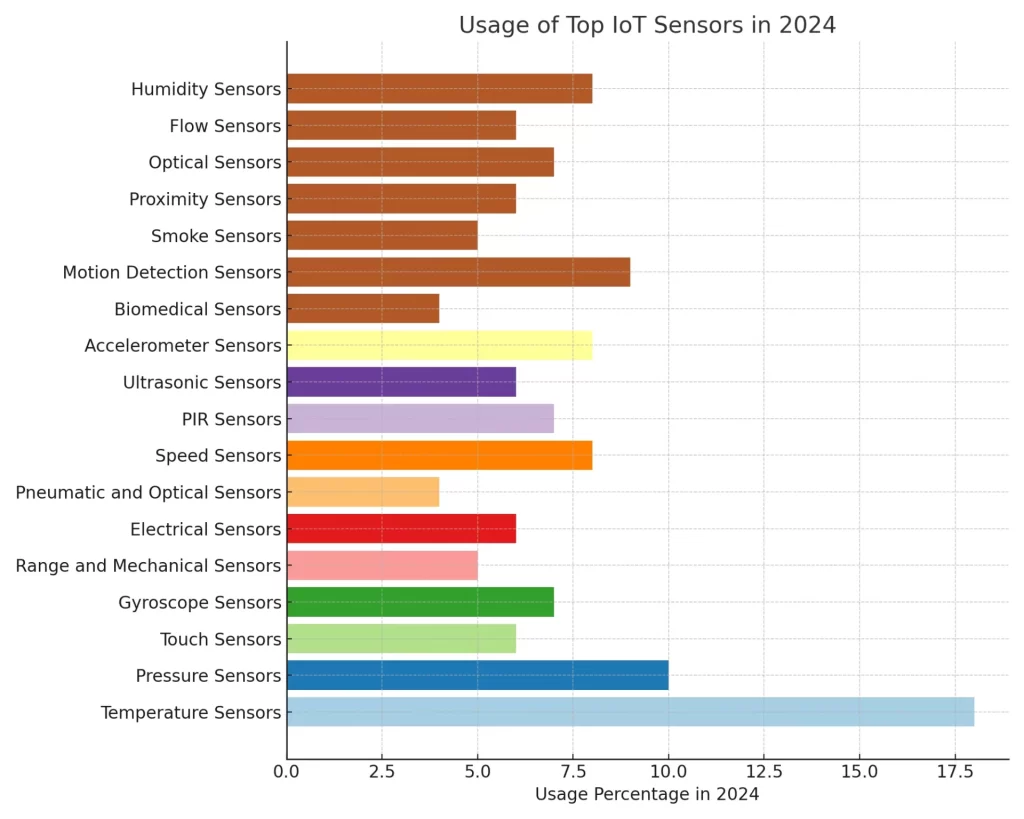
Types of IoT Sensors and It’s usages
Types of IoT Sensors and It’s usages on Real time Data 2024 on Graph Given below
Purpose of IoT Sensors
The use of IoT sensors can greatly enhance various sectors and make people’s lives better due to the increased ability to share and use data in real-time.
IoT sensors help individuals, organizations, and businesses get real-time data, automate procedures and make informed decisions that improve organizational effectiveness and productivity. This capability is especially useful in logistics where more than eight types of IoT sensors are deployed to optimize supply chain operations.
The configuration of the sensors is crucial for the accuracy and efficiency of the system, and only with the help of experienced specialists, it is possible to create a logistics application that will bring tangible results to a business.
For instance, in smart homes, the IoT temperature sensors enable users to regulate temperatures in rooms from a distance, thus increasing energy effectiveness. Likewise, the light sensors control the intensity of the light depending on the available natural light, and the motion sensors in security systems help in better safety.
When IoT applications use a combination of sensors selected to meet certain requirements, they can provide purposeful and valuable outcomes in various industries.
Suggestions and Security Things One Should Know
- Ensure Proper Integration: IoT sensors have to be set up and integrated into a system when they are to be used. Wrong settings may cause wrong data collection, low efficiency and even system failures.
- Emphasize Data Security: As IoT sensors handle personal data, the cybersecurity of the system is paramount/vital. Ensuring encryption of the data, achieving secure authentication and frequent updating to the software would help a lot in safeguarding the authenticity of the data.
- Monitor Sensor Accuracy and Regular Maintenance: There is also a possibility that the sensors will degrade in their accuracy because of environmental factors or just ordinary usage over some time (as we know time has crushing powers for nonliving objects). The data gathered from the sensors cannot be trusted to be accurate at all times which therefore requires maintenance and calibration now and then.
- Account for Scalability: In the future, when IoT systems expand, there may be a need to include new sensors and devices in the system. It is necessary to make sure that the system is developed in a way that integration problems will not appear as the number of people who need the system increases.
- Consider Power Consumption: The majority of IoT sensors are equipped with batteries and the amount of energy used is proportional to the type of the sensor and its frequency of data transmission. Sensors should be employed sparingly and the activity of those used should be minimized to save as much energy as possible and if possible low energy sensors should be used.
Conclusion
The use of IoT sensors is becoming more and more popular in industries and among people for collecting, processing, and using information about the environment and for improving performance living standards in smart homes. From changing the face of healthcare and logistics to improving homes, IoT sensors offer useful real-time data that fuels innovation. The said sensors not only enhance automation and monitoring but also enable efficient data acquisition and decision-making in integrated systems. With the development of IoT, the incorporation of various types of sensors will be crucial for creating flexible systems for the increasing requirements of a digital society. When it comes to IoT sensors, industries are sitting on a goldmine of possibilities that can pave the way to a smarter world.
Find More About IOT