The Impact of IoT on Industry 4.0: Driving Efficiency, Innovation, and Productivity in 2024
The impact of IoT on Industry 4.0 is transforming business operations in 2024. By integrating connected devices, industries like manufacturing, healthcare, and logistics are improving efficiency, boosting productivity, and driving innovation to new heights . Industry 4. 0 (also referred to as smart manufacturing (SM)) is a revolutionary shift within the manufacturing industry, being the fourth industrial revolution.
This transformation is characterized by the fact that the integration of IoT technologies is ubiquitous across all aspects of production.
What distinguishes Industry 4.0 is its vision of intelligent factories that surpass simple automation, facilitating the vision of intelligent factories that exceed more than automation. If we are talking example of Impact of IoT industry 4.0 Amazon utilizes IoT devices, such as RFID tags and smart sensors, to track packages in real-time
Advantages of applying the impact of IoT on Industry 4.0
Today, digitalization is considered to be crucial in various fields of present-day business activity. However, organizations that adopt Industry 4. 0 and leverage the impact of IoT on Industry 4.0, along with Big data and Artificial intelligence experience significant positive change in productivity, customer satisfaction and discovery of new business opportunities.
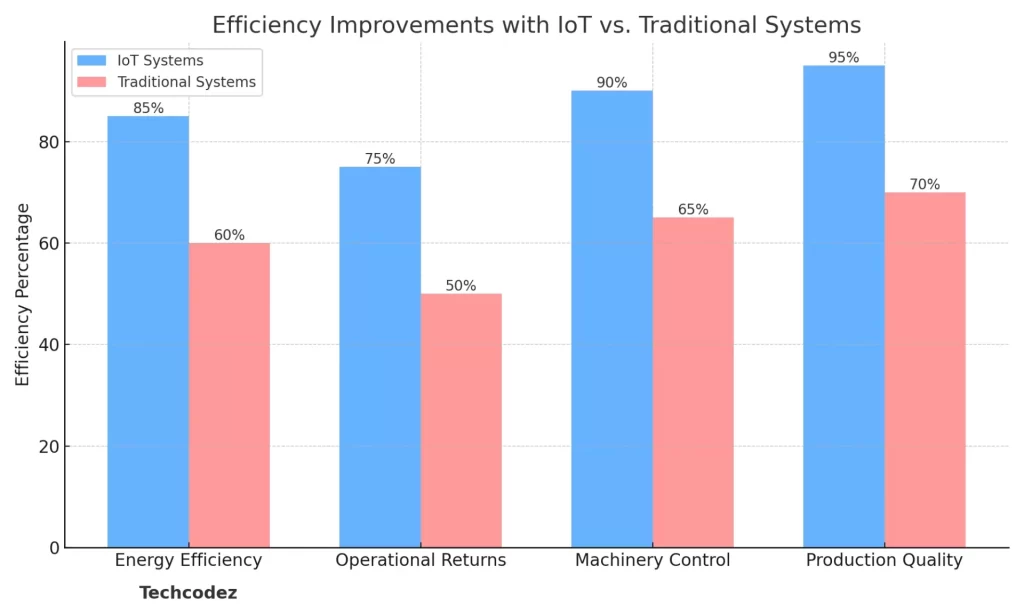
Enhanced Energy Efficiency
The impact of IoT on Industry 4.0 allows for real-time tracking of Energy use and carbon dioxide emissions tracking in real-time application enhances the efficiency of energy management programs in production.
Improved Operational Returns
This makes automation cost-effective, improves service delivery, and also decreases the need for corrective maintenance due to quick and accurate diagnostics.
Enhanced Machinery Control
Ongoing surveillance of machinery guarantees efficient running, identification of problems and avoidance of possible risks and unsafe working conditions, which ultimately leads to predictive maintenance.
Elevated Production Quality
It facilitates strict quality control measures, reduces human interference, reduces human error and ensures protection against supply chain frauds, loss or replacement of products.
Enhanced Productivity and Efficiency
Integration of machines allows them to communicate effectively, reducing the overall time taken to complete operations.
Real-time Decision Making
Sensors collected information for timely adaptations and quick problem solving.
Increased Flexibility and Agility
Modern smart factories powered by the impact of IoT on Industry 4.0, can effectively manage fluctuating customer requirements and adjust production with high levels of flexibility.
At the heart of this evolution is the Internet of Things (IoT), where smart sensors are fitted on machines, products, and materials to monitor data. The above information is then fed into a common network and delivers on the spot real-time information on every step of the manufacturing process.
Main Cybersecurity Challenges of IoT Manufacturing
There is much to gain from integrating it into manufacturing processes, but new threats and risks abound, and they cannot be ignored. Here are the primary concerns:
Data Privacy
These connected devices as part of the impact of IoT on Industry 4.0, produce large volumes of data that include simple and complex information like production processes, product designs and customer information. It is crucial to have strong protection measures to ensure that only authorized users get access to the app and it is not misused.
For example, industries operating in the European Union and California require data protection laws such as GDPR and CCPA, which means that manufacturers have to protect the data securely and ensure proper user consent.
Network Security
impact of IoT on Industry 4.0 brings a rapid growth of connected devices increases exposure to malicious actors, offering more vectors of attack. Weaknesses in any kind of device can lead to threats affecting the whole network.
Some IoT devices might have poorly implemented encryption or use insecure communications protocols, making them vulnerable to data interception or theft.
Risk of Cyber-attacks
Interconnected manufacturing systems become a focal point of cyber threats that have the potential to interrupt production, compromise information and cause losses.
IoT devices can be threatened by different types of malware and ransomware that can hinder the functioning of an organization and encrypt data for a hefty sum of money.
Strategies for Mitigating Risks:
To mitigate these cybersecurity risks effectively, manufacturers should implement the following strategies…
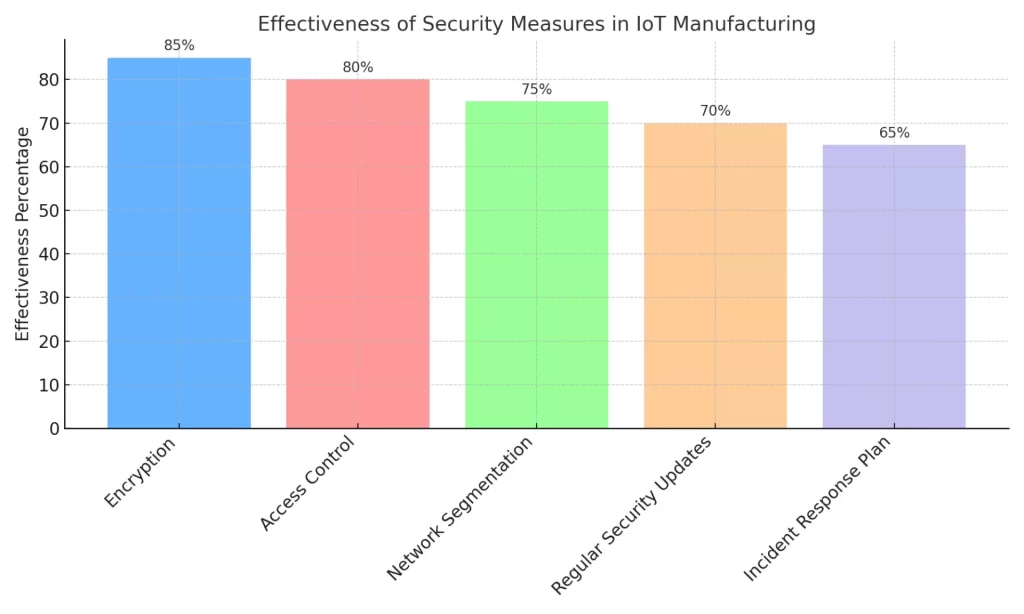
- Strong Access Controls
- Regular Security Updates
- Network Segmentation
- Encryption
- Security Awareness Training
- Vulnerability Management
- Incident Response Plan
These are some of the cybersecurity challenges that manufacturers are bound to face when implementing IoT technology as part of the impact of IoT on Industry 4.0 in their production processes. The following protective measures can help the manufacturers to protect themselves from these challenges.
If these protective measures are put in place, manufacturers can be in a position to tap into the benefits of IoT in the production of their products without having to worry about the challenges mentioned above.
Improvements with IoT vs. Traditional Systems
Effectiveness of Security Measures in IoT Manufacturing
Conclusion
Smart sensors, coupled with the impact of IoT on Industry 4.0, can significantly improve production, reduce time lost to faults, and potentially make manufacturing more environmentally friendly. This intelligent future is not only about doing things faster and better but also about being flexible and ready to meet new challenges that the market puts in front of manufacturers. Though there is always the danger of hacking, it is possible to implement strong measures to secure data and the network. Industry 4.0, thence enabled by IoT, offers a window into a smarter, more sustainable and adaptable manufacturing environment.
Learn more about IOT