Mastering IoT Protocols : Essential Guide to Zigbee, Z-Wave, and Wi-Fi
IoT connects physical objects/devices through the Internet, making the IoT protocols responsible for the connectivity and data exchange of these objects. It is crucial to understand the different IoT protocols available on the market because organizations need to find the most suitable solutions for their business. In this guide, the reader will find information about the IoT protocols for smart homes and their uses.
What is a Smart Home Protocol?
A smart home protocol comprises guidelines that control and coordinate communication among devices within a smart home, allowing them to share information smoothly.
In other words, it serves as a kind of ‘interface’ between the devices and enables them to work with each other, no matter which company they belong to. These standards allow smart home products from different manufacturers to work together in a harmonized manner so that the efficiency of such products in any smart home increases.
These protocols facilitate the authentication of devices, secure data transfer and provide associated techniques for error checking on device communication. These also make the interactions of the devices reliable and secure. There are several smart home protocols, and some of them are Z-Wave, ZigBee, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), Ethernet, Thread and Matter.
Significance of IoT Protocols
Why IoT protocols are important?
An IoT protocol is a set of standards that define how different IoT devices should be communicating with each other independent of differing manufacturers and platforms. These protocols are used for data transfer in IoT and are crucial in the operation of IoT projects across the globe. If there were no specific protocols, the devices would not be able to communicate, which would be counterproductive to the IoT applications.
The Difference between IoT and Traditional Internet Protocols
There are normal internet protocols like HTTP, FTP, etc. which are developed for general internet usage and then there are IoT protocols which are developed specifically for IoT devices taking into account range, data payload, and energy constraints.
The main difference between IoT and conventional protocols is communication type. Traditional standards often employ connection-oriented protocols, such as TCP, whereas IoT protocols support both connection-oriented and connectionless approaches.
This dual support means more options for data transfer in IoT, and more versatile solutions in different IoT contexts.
How IoT Protocols for Smart Homes Work?
In connection-oriented protocol, devices first make a connection before transmitting data and hereafter ensure accurate transmission of data in the right order.
On the other hand, connectionless protocols allow data to be transmitted without prior establishment of a connection and are used when speed is important and few data packets can afford to be lost.
For smart products to securely and seamlessly connect, they have to speak the same language using compatible communication interfaces. These set out how signals are communicated between devices to elicit activities such as the operation of lights.
It is important to understand the difference between the protocols because each of them has its strengths and weaknesses depending on the context of using it when choosing devices in an automated environment.
Common Smart Home IoT Protocols
Key Features, Advantages, Disadvantages and Security
1. Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi is a wireless networking technology that implements the IEEE 802.11 standard and works mainly in the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands. Common in IoT smart home devices, it can handle data-heavy applications.
- Benefits: Extremely flexible and with broad coverage, Wi-Fi is compatible with most smart home devices such as video streaming with adequate throughput for data-intensive devices.
- Limitations: Wireless Local Area Network is a power-hungry protocol that is not suitable for many battery-powered devices. It may suffer from signal interferences due to physical obstacles and other devices operating on the same frequency.
- Security: Wi-Fi uses WPA2 and WPA to encrypt data and security is only as good as the password used and firmware updates to counter any security threats.
2. Bluetooth Smart or Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE)
Bluetooth and BLE work at 2.4 GHz and are intended for low-power wireless communication in short ranges suitable for battery-powered smart devices.
- Benefits: Because of its low energy consumption, BLE is suitable for use in smart locks, sensors, and light bulbs. Bluetooth also supports other features but at the same time, it consumes more power.
- Limitations: Short range of operation due to which the coverage area is restricted and not suitable for devices that require long-range or high data transfer.
- Security: Data is protected with AES-CCM encryption, though security relies on up-to-date firmware to mitigate vulnerabilities.
3. Zigbee
It (Zigbee) is a low-power radio frequency standard working at 2.4 GHz with mesh network topology where devices are nodes and can reroute if nodes are lost.
- Advantages: Zigbee is a good fit for IoT protocols due to its low power consumption and mesh capabilities, and can be used for applications such as smart home devices including lighting, thermostats, and sensors. Device communication is one of the most reliable features in the system.
- Restrictions: Restricted mobility within huge houses; to expand the reach, more repeaters or routers are needed, which increases the costs and the design of the network.
- Security: Zigbee uses AES-128 encryption with manufacturers updating firmware for secure messaging.
4. Z-Wave
Z-Wave uses the sub-GHz frequency band (<1 GHz) and all devices in the network can be nodes, which means that data can be rerouted if a node is not functioning.
- Advantages: Low power consuming and well-known mesh network, it has a self-healing topology which is suitable for smart lighting, security, and thermostat applications.
- Limitations: Z-Wave may have some compatibility issues with other smart devices due to the fact that it is proprietary.
- Security: It has AES-128 encryption and supports two-way device authentication, and security is preserved through over-the-air (OTA) updates.
5. Advanced Message Queuing Protocol (AMQP)
AMQP stands for Advanced Message Queuing Protocol and it is an open standard that is meant for message-oriented communication middleware, so that no matter which system you are using or which message broker you are using. AMQP is well known for its reliability, security, and its ability to keep the connection alive across distances or poor networks where devices may not always be available. Good choice for smart home IoT protocols in cases of need.
5 Essential IoT Protocols for Smart Homes

Comparing Top IoT Protocols for Smart Homes
Comparing Top IoT Protocols for Smart Homes: Range, Efficiency, Compatibility, and Security
| Protocol | Range | Energy Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
| Wi-Fi | High (up to 100m indoors) | Low (high power consumption) |
| Bluetooth (BLE) | Short (up to 10m) | High (low power consumption) |
| Zigbee | Medium (10-20m indoors) | High (low power consumption) |
| Z-Wave | Medium (30-40m indoors) | Moderate |
| AMQP | Varies (depends on network) | Varies |
| Protocol | Compatibility | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Wi-Fi | Low (high power consumption) | Data-intensive applications |
| Bluetooth (BLE) | High (low power consumption) | Short-range devices (locks, bulbs) |
| Zigbee | High (low power consumption) | Smart home automation (lighting, sensors) |
| Z-Wave | Moderate | Home security, lighting |
| AMQP | Varies | Reliable message transfer across devices |
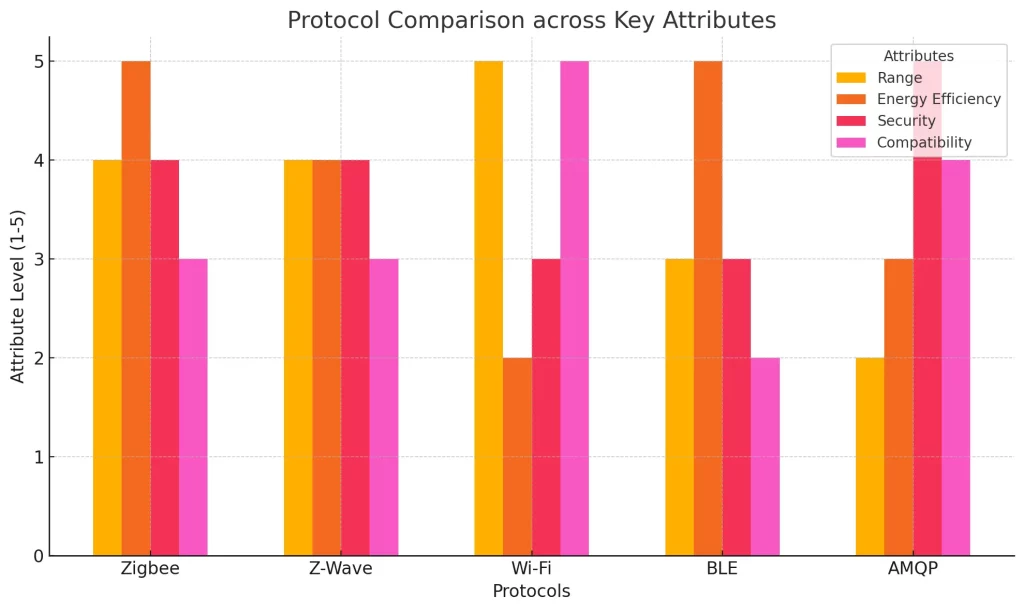
IoT protocols across attributes
Protocol Comparison Across Key Attributes Rang , Energy Efficiency , Security and Compatibility
Summary
Mastering the various IoT protocols such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, and Z-Wave is essential for building an efficient, reliable, and secure smart home ecosystem. Each protocol offers distinct advantages; Wi-Fi is best suited for bandwidth for data-hungry applications, while Zigbee and Z-Wave are designed for low power, mesh networking and support extensive networking. Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), which is energy-friendly, is ideal for small devices. When these differences are outlined it helps their users make better decisions concerning the improvement of the interoperability, security and functionality of smart home systems. The understanding of these protocols allows individuals and organizations to develop the smart and flexible home solutions, future proof for specific needs and encourage an innovative and integrated living environment.
FAQ
Why does Wi-Fi have lesser compatibility with battery-powered smart home devices?
In terms of power consumption, Wi-Fi is much greedier than protocols such as Zigbee, Z-Wave or Bluetooth Low Energy. This high power demand also makes Wi-Fi less compatible with battery-powered devices.
Which technology is better Bluetooth or Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE)?
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) is generally more suitable for smart home devices that are low-power devices that need to cover short ranges.
How Zigbee, Z-Wave and Wi-Fi are different in security features?
For data protection, Wi-Fi commonly uses WPA2 or WPA3, and both Zigbee and Z-Wave use AES encryption.
Is it possible to have more than one IoT protocol, for instance, Wi-Fi and Zigbee in a smart home system?
Indeed, there is the possibility of incorporating more than one IoT protocol into a smart home system, which is usually achieved by using an intermediary device to communicate with the IoT devices.