Top IoT Security Practices in 2024: Safeguard Your Smart Devices
Keep your smart devices safe in current era with these top IoT security tips. Learn simple steps to protect your devices and your network from potential threats . IoT Security is the process of protecting IoT devices and the networks upon which they run. Its main purpose or goals are to safeguard user anonymity, preserve data integrity, safeguard devices and related structures, and guarantee the continuous and efficient operation of the IoT environment. Internet of Things security is a vast and significant field, primarily because IoT is an expansive concept that integrates internet connectivity into devices designed for particular purposes. This emerging field of study has numerous possible uses and therefore raises issues related to security.
Overview
The Internet of Things (IoT) is not limited to “smartphones” or “computers” but is deeply integrated into modern-day “kitchen appliances”, “climate control” and “security systems” in smart homes, smart televisions and smart cars.
IoT has impacted how we perform our tasks, sustain our lives and engage in leisure activities, collecting massive amounts of information about our whereabouts, purchases, media preferences, and network surroundings.
Hence, the development of the IoT security guidelines and their implementation is necessary to protect the devices, users and networks from cyber threats.
IoT security can be defined as the ability to secure individual IoT devices with the best security practices, as well as the overall security of the network environment. Regardless of the IoT device type that is connected to a network, its safety has to be governed along with other network components for the best result.
What is IoT Security?
IoT Security is aligned with securing the devices and the networks in the IoT ecosystem. It involves preventing the threats from these devices on the network. This means that since anything that connects to the Internet can be attacked, IoT devices are not an exception. Threat agents use remote access to accomplish objectives by tactics like obtaining their victims’ credentials or capitalizing on vulnerabilities. Preventing such threats to these devices is what IoT security is all about.
Types of IoT Security
IoT security is a layered one, the goal of which is to protect devices, networks and data. Security responsibility is divided between the users and manufacturers.
Network Security
If we are talking about IoT Security Network Security is first one This involves protecting the overall infrastructure of IoT networks through several measures:
- Establishing a strong network perimeter
- Enforcing zero-trust architecture: Supposing that every device and every user is a threat that needs constant validation of its access.
- Securing network communication: Guard data transfer between devices by making the communications secure through the use of encryption.
Device Security
If we are talking about IoT Security second one is Device Security Device security emphasizes the protection of individual IoT devices:
- Embedded security agents: Using lightweight software to watch the device’s activity and to detect abnormal activity.
- Firmware hardening: Testing and constantly updating the device software and the software’s ability to not have any holes in it.
- Secure boot process: Confirm the authenticity of the device’s operating system before the device runs it.
Data Security
If we are talking about IoT Security Third one is Data Security
- Data encryption
- Data privacy: Measures to be taken to avoid leakage of information to unauthorized persons.
- Data integrity: Checksum and similar methods of maintaining the consistency and accuracy of the data.
How Does IoT Security Work?
As IoT devices store and transfer data through the cloud, the security protocols needed for IoT devices are different from those of conventional mobile devices. Unlike mobile operating systems such as iOS and Android, IoT devices are normally not developed with set security policies.
A large part of IoT information is stored in the cloud, so, for example, if an attacker receives access to a user’s account, he will be able to use the information received to commit identity theft or other violations of privacy rights. To date, there is no perfect solution for IoT security; however, cybersecurity specialists pay attention to the best practices in coding and propose measures to strengthen the protection of clouds.
The Role (Necessity/Importance) of Security in IoT
It is universally accepted that IoT is one of the biggest security threats to consumers, businesses, and governments. When you have billions of devices connected globally, the exposure to threats has also grown exponentially.
GSMA Intelligence estimates that IoT devices will be 25 billion by 2025 and therefore a need to employ better security solutions.
Although IoT is a rich source of value and convenience, it has many threats, which stem from the lack of security considerations during the device design. The functionality of the device is given more importance than its security and thus devices can easily be exploited for instance by setting a weak password.
This reality underlines the necessity of IoT security. The increase in the use of IoT devices requires more security not only for the devices but also for the network they are using.
Common IoT Security Challenges/Concerns
Increasing the use of IoT devices in various industries has also increased security issues, which are not given due consideration. As opposed to conventional information technology systems, numerous IoT devices have poor security frameworks, which makes them vulnerable to hacking. Below are the top 12 common IoT security concerns:
Poor Vulnerability Testing
Most IoT devices are not designed with security in mind; hence, they have not undergone sufficient vulnerability tests. This inability to detect possible vulnerabilities before the deployment of the devices makes the devices vulnerable to cyber threats.
Unpatched Vulnerabilities
IoT devices are frequently powered by old firmware with open holes that cannot be patched due to the difficulty of applying updates or because no patch is available. A lot of devices stay online for years without receiving important security patches.
Default Passwords and Weak Authentication
These connected devices are often sold with default passwords which are not changed by the users most of the time. Although passwords are changed from time to time, they are usually poor, which makes the devices vulnerable.
Old Firmware and Software
Another issue is that IoT devices are deployed and then rarely changed, meaning that they will not have the latest software patch for a newly discovered exploit or risk/threat. This lack of regular firmware or software updates makes these devices the perfect target for an attacker.
Poor Control over Devices and Their Configuration
IoT devices are usually implemented without the IT department’s approval, and this results in a blind spot and poor device management. This results in what is known as “Shadow IoT,” which makes it hard to protect networks.
Limited Security Integration
This has made it difficult to incorporate IoT devices into the current security frameworks due to the many types of devices that are currently in the market. Most of the devices do not have the compatibility required for integration with conventional security systems.
Legacy Assets
A large number of industries have deployed IoT devices that were developed years ago and do not meet today’s security standards. The costs involved in replacing or upgrading these devices are high and the process is complicated hence organizations retain outdated devices that are vulnerable to attacks.
Data Privacy Concerns
The huge amount of data produced by IoT devices poses a major threat to privacy.
Lack of security measures leads to leakage of information and unauthorized access and use of the information.
Complex Environments and Overwhelming Data Volume
This is because IoT ecosystems are made up of many devices, platforms, and protocols, which cause complexity. This complexity leads to security issues where they are not well addressed.
IoT devices produce a lot of data and this is problematic for conventional data management systems. Maintaining the security and accuracy of data in such settings is difficult.
APIs as Attack Vectors
APIs utilized in IoT contexts are often attacked by using different techniques like SQL injection, DDoS, MITM, etc.
How to Use IoT Security in Three Steps
The following are the steps that organizations should follow to construct the IoT security strategy that will prevent attacks on IoT devices…Below are three crucial steps to developing a comprehensive security plan for IoT ecosystems:
Step 1: Device Discovery
The first measure of protection with IoT devices is to determine all of the connected devices in the network. Device identification and discovery tools can automate this process and execute three critical security functions:
- Autonomous Detection: It is possible to continuously and automatically detect, profile and classify IoT devices connected to the network.
- Real-Time Inventory: It is also crucial to keep track of all the devices in order to have a clear understanding of the general picture of IoT.
- Risk Intelligence: Important to indicate the risk associated with each of the device classes by continuously looking for likely attack vectors.
Step 2: Risk Analysis
The next important process that takes place after the discovery of all IoT devices is the risk assessment. This involves evaluating vulnerabilities and potential threats associated with each device:
- Vulnerability Assessment: Conduct periodic vulnerability assessments on devices and install missing /new updates/patch on devices to eliminate security risks.
- Threat Modeling: Discuss the possibility of how attackers can leverage IoT devices to gain entry into certain organizations or Access and Control to launch massive attacks.
- Risk Prioritization: Determine which devices present the greatest risk and then rank them according to their criticality and vulnerability to threats.
Step 3: Monitor, Protect, and Enforce
After identifying and analyzing risks, the final step is to monitor the IoT environment, enforce security policies and protect the network…
- Continuous Monitoring: It is necessary to incorporate mechanisms that provide timely identification of any attempts made, deviation or unauthorized access of the device.
- Network Segmentation: Isolate IoT devices so they do not communicate with other devices in the organization or the rest of the network.
- Security Enforcement: Embrace a strict security regime that ensures regular software updates as well as proper incorporation of security parameters like two-factor verification and secure protocols.
- Incident Response: Make a specific disaster response policy that would be used in case of cyber security incidents related to IoT.
How to Meet IoT Security Needs
It means that meeting IoT security requirements requires a solution that would provide visibility, segmentation, and protection of the entire network.
An integrated security approach as represented by a holistic security fabric model is crucial for IoT ecosystems. Key elements include:
- Learn: To ensure that the network is fully secured, visibility must be achieved to authenticate and classify IoT devices to create risk profiles for the devices and group them.
- Segment: Categorize IoT devices by security risks and define policy-based groups to improve security control.
- Protect: Control and regulate security policies depending on the activity at various stages in the network, to ensure the security of IoT devices.
Introducing Effective Authentication and Authorization Processes
Security is important for IoT devices and especially the authentication process.
IT administrators have to decide on the best form of authentication and authorization; one-way, two-way or three-way in accordance with the latency and data needed.
Most IoT devices lack proper authentication and in most cases, they use default passwords that can be easily cracked. In the authentication process, IoT device certificates have a significant role in ensuring security in comparison to the traditional authentication mechanisms.
What Attacks IoT Devices are Most Vulnerable To?
IoT devices are especially susceptible to numerous attacks because of their specific features and the absence of intensive security solutions. Below are some of the most common attack types that target IoT devices:
Exploitation of Firmware Vulnerabilities
Firmware can be described as the preliminary software that manages the hardware of devices. In many IoT devices, firmware can be considered as an operating system of the device. However, IoT firmware is not as secure as modern operating systems, it does not contain such complex protection mechanisms. These devices are often laden with known vulnerabilities, some of which cannot be updated, which makes them an easy or juicy target. This lack of security makes IoT devices open to exploitation where hackers look for such firmware flaws.
Credential-Based Attacks
A large number of IoT devices are deployed with default administrator accounts and passwords. These default credentials are usually easy and poor, and most IoT devices use the same logins across the devices. Sometimes these credentials are not changed and this poses a problem to the device. This is because the default settings are well known to the attackers and they can easily log in by assuming the password.
On-path attacks
These are also known as Man-in-the-Middle attacks.
The on-path attack is where an attacker takes the middle between two communicating parties, for instance, an IoT device and a cloud server. They control the flow of communication between the two parties without the consent of the two involved. If the data is not encrypted, the communication can be exploited by the attackers since the data is sensitive.
Physical Attacks: Hardware
Smart devices like security cameras, stoplights, and alarms are typically deployed in stationary and exposed settings. In this case, an attacker can easily get hold of an IoT device and try to compromise the hardware to get hold of information or control the device. This attack only targets one device at a time but an attacker can use the compromised device to gain more control of the network.
IoT Security Threats by Percentage in 2024
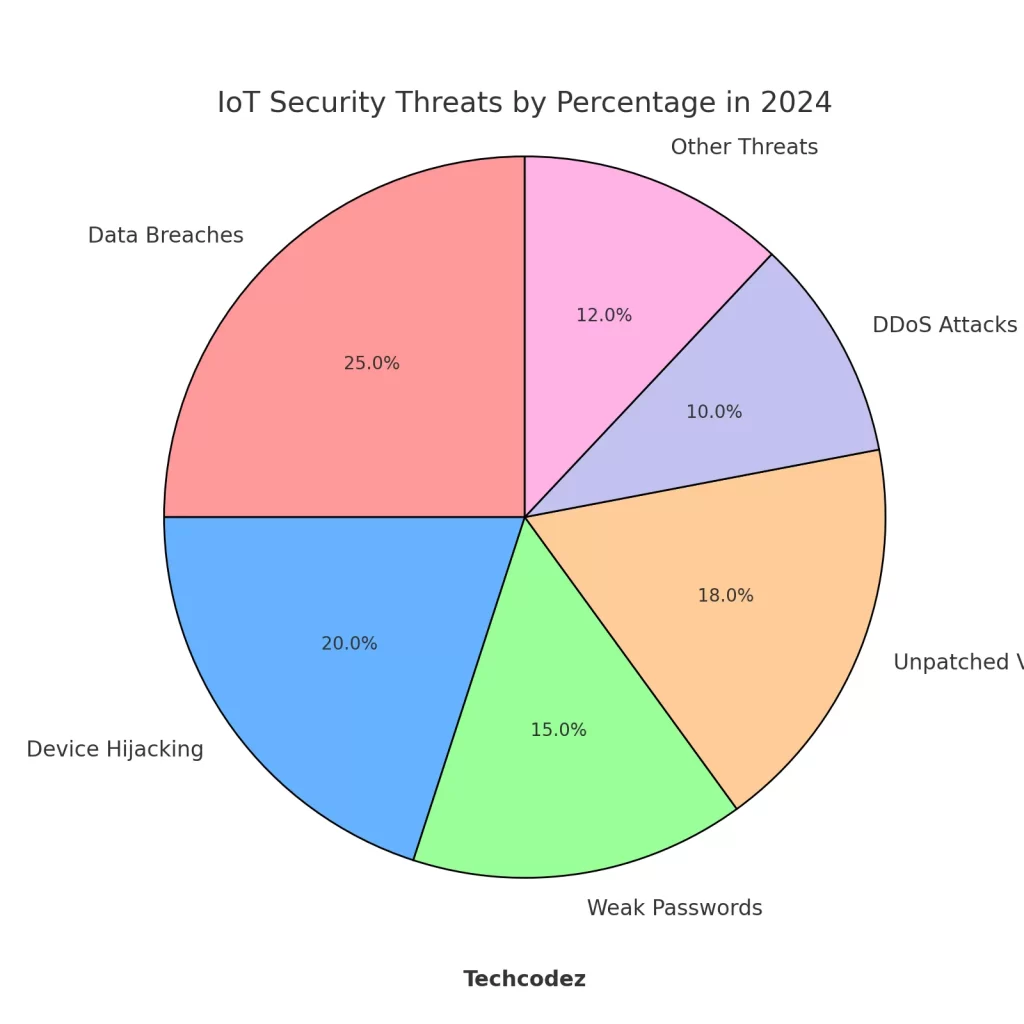
This Graph showcase of top IoT security threats in 2024, including data breaches, device hijacking, and weak passwords .
IoT Security Measures in IoT Devices
Security is a paramount concern for the IoT, and there needs to be a strong approach to protecting information in the cloud and ensuring that information remains valid and unaltered as it passes through the infrastructure.
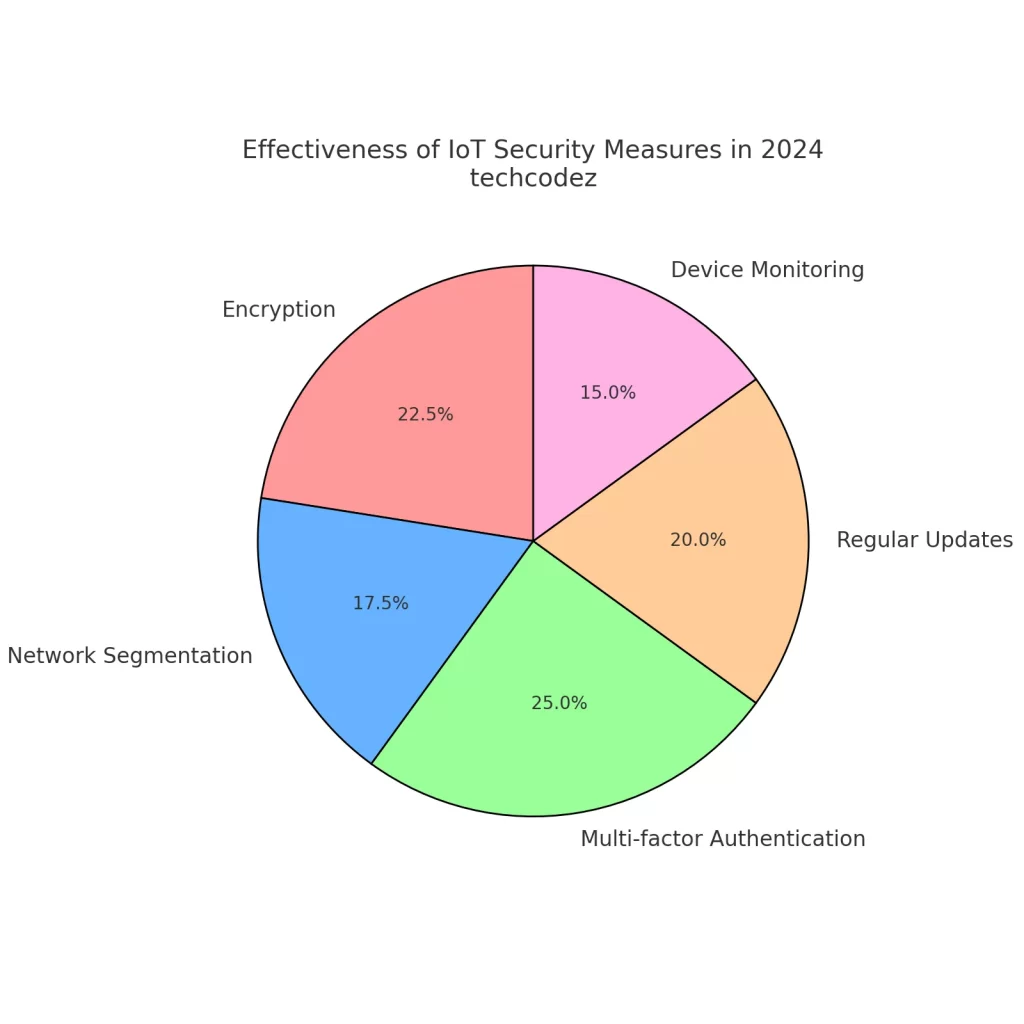
The following best practices can enhance IoT security within an organization
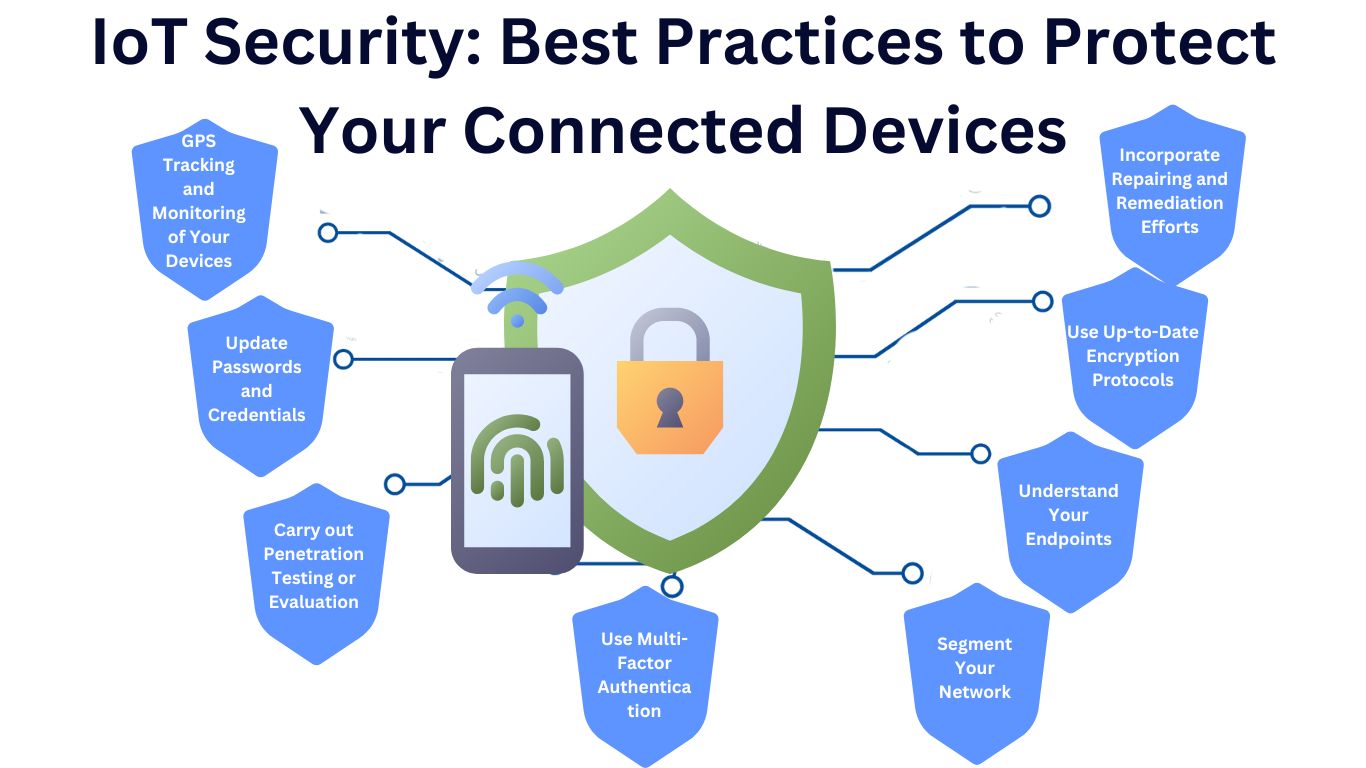
GPS Tracking and Monitoring of Your Devices
The devices are used in managing an organization; it is important to understand each device and how it works. It becomes crucial to install continuous monitoring software that would facilitate device monitoring, discovery, tracking and management, thus protecting the organization against future attacks.
GPS Tracking and Monitoring of Your Devices
Patching and remediation entail taking time to modify the code of other connected devices to enhance security. When you are planning to connect a piece of hardware to the network, consider whether the device can be updated to fix vulnerabilities in the future. When it comes to devices, it is important to take into consideration the limitations and the multifaceted nature of devices so as not to overlook any relevant approaches and have a detailed plan in place before the start of its use in the classroom.
Update Passwords and Credentials
Contrary to the fact that there appears to be nothing more old-fashioned, changing passwords is crucial since many devices come with default vendor-supplied passwords. These default credentials are not hard to guess and cybercriminals can easily use them. Password refresh and exercise of good password practices are important for the security of the devices. This playing important role for IoT Security .
Use Up-to-Date Encryption Protocols
Having data that is not encrypted means that any criminal will have a chance of accessing all the sensitive information they require. This should involve encrypting all data in a network by the most recent encryption techniques to ensure that the data is not understandable by anyone who has no business interacting with the data in the network.
Carry out Penetration Testing or Evaluation
Smart devices are more prone to attacks because of their design and focus on usability and connectivity. Before the deployment of IoT devices, perform penetration testing or evaluation on the hardware, software, and other devices. It also assists in the exposure of the weaknesses, the evaluation of security measures and the review of agreement with the law to avoid severe future risks.
Understand Your Endpoints
Each connected device that is created is a new endpoint, which can lead to multiple vulnerabilities for hackers to exploit. IoT endpoints are at high risk and need to be profiled and recognized by the organizations to ensure a secure connection. Invest in endpoint security solutions that include antivirus software, mobile device management, security patches and encryption.
Segment Your Network
Using network segmentation as a countermeasure, one can prevent device hacks before they occur. Subdivide the networks into smaller sub networks to lock out the intruders and restrict their access to other sections. This reduces the chances of individuals accessing sensitive information and boosts security.
Use Multi-Factor Authentication
This extra layer of security helps to protect the IoT networks to allow only those with the right credentials to interact with the devices.
Adoption of these best practices can greatly improve the IoT security of devices, users and networks protecting them from cyber threats. Undeniably, IoT devices are beneficial when implemented in society; however, the increase in the use of these devices has led to numerous security issues. As highlighted above, following the best practices mentioned will enable organizations to enhance IoT security. Nevertheless, the threats are dynamic and organizations need to keep up with the trends and developments in the cyber world.
Tools to Secure IoT Devices
- ForeScout Platform: It protects IT, IoT, and OT devices in a network. In this way, it provides end-to-end protection by applying the zero-trust model.
- Microsoft Defender for IoT: It provides enterprises with a solution for managing, discovering, and securing devices. It comprises services like threat detection of networks and devices as well as identification of assets, around the clock.
- Asimily: It offers a complete package of solutions suitable for healthcare facilities.
- AWS IoT Device Defender: It helps administrators check compliance with security requirements, including authentication and permissions, for IoT devices.
Secure tools will allow organizations to decrease the vulnerability of IoT to cyber threats by recognizing and mitigating these areas of concern and implementing them successfully; to protect the privacy of data, functionality of devices, and overall performance.
Benefits of IoT Security
Network Protection
IoT security enables the entire network to be secure to prevent threats such as DDoS attacks that are detrimental to IoT devices and data.
Privacy Protection
Security solutions protect the privacy of the users by excluding the possibility of surveillance, and theft of data and tracking of devices so that the privacy of the users is not violated.
Scalability
A good IoT security framework is flexible, meaning that as the number of IoT devices increases within an organization, it can easily accommodate the change without compromising on security measures.
Device Protection
IoT security makes certain that they are used optimally and are not infected by viruses, hacked, or accessed by unauthorized persons hence their durability is guaranteed. This protection also gives mental peace, especially in smart homes
FAQs
What is IoT Security?
Internet of Things security is the practice of protecting IoT devices as well as the networks they connect to from cyber threats and cyber-attacks.
Why IoT Security is Important?
Security is paramount for IoT because the majority of IoT devices are vulnerable to cyber-attacks. When these devices connect to networks, they are often invisible to standard security solutions, leaving them open to attacks especially when they transfer unencrypted information.
How does Cloudflare aid in securing IoT devices?
API Shield from Cloudflare defends IoT gadgets by maintaining stringent identity management with client certificates and IoT API schemas validation, making IoT environments immune to cyber threats.
How are IoT devices involved in DDoS attacks?
The IoT devices are usually left open and unsecured, making them an easy target for hackers to recruit them into a DDoS attack. A DDoS attack is one in which many devices flood the targeted system with traffic, which results in a shutdown or slowdown. Since every IoT device is assigned an IP address, these attacks become challenging to prevent since there is a massive number of devices. An example of a huge botnet, known as the Mirai botnet, was formed with the help of hacked IoT devices.
Learn more about IOT